Choosing What Scales: React Native Vs Kotlin Multiplatform
October 23, 2025
Introduction
The foundation developers choose to build on shapes every swipe and scroll before it even reaches the user.
Mobile applications have evolved from being simple utilities into strategic investments that drive user engagement, boost business performance, and strengthen brand loyalty. Spanning Android, iOS, and other platforms, they are now inclined towards shaping functionality, long-term sustainability, and accessibility for modern businesses.
The framework choice directly impacts how project teams operate. Using the same code across several platforms, native API access, backend system interface, and development tool support all have an impact on how rapidly teams can build, debug, and maintain programs. Furthermore, it ensures that projects are completed more quickly, are optimal for users, and are easier to extend or upgrade in the future.
This blog will look at two popular mobile development solutions: React Native and Kotlin Multiplatform. It is intended for development teams, product managers, IT decision-makers, and skilled Android developers who wish to leverage developer tools, comprehend trade-offs, and make wise choices while creating excellent native apps and cross-platform solutions. It will aid developers and stakeholders in choosing the right framework that fits their long-term strategy, client requests, and project specifications.
Understanding the Frameworks
React Native
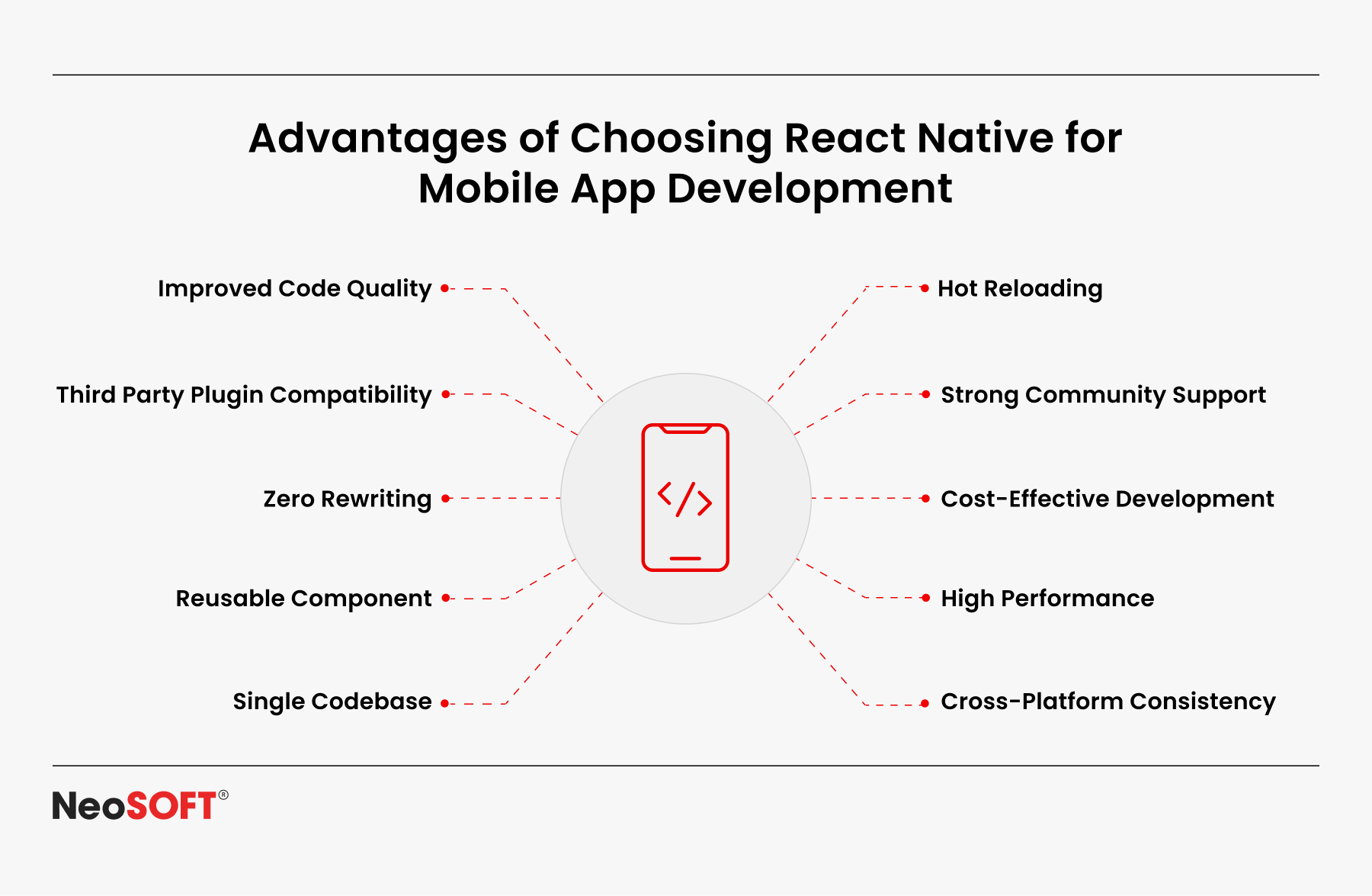
React Native, developed by Meta, is a declarative UI framework that enables developers to write applications in JavaScript and React for both Android and iOS. Also, it enables rapid prototyping and excellent cross-platform mobile app development using its vast library ecosystem and pre-built components.
Key advantages include:
- A single codebase can provide cross-platform compatibility, which reduces platform development complexity and time.
- Hot reload for faster debug cycles and improved workflow efficiency.
- A large community with active contributions, extensive documentation, and reusable libraries supported by global developers.
- Simple connection with web applications, iOS, and Android developer tools, native code, and backend APIs.
- Businesses that want to rapidly build apps that run on different platforms without maintaining numerous repositories are adopting React Native significantly.
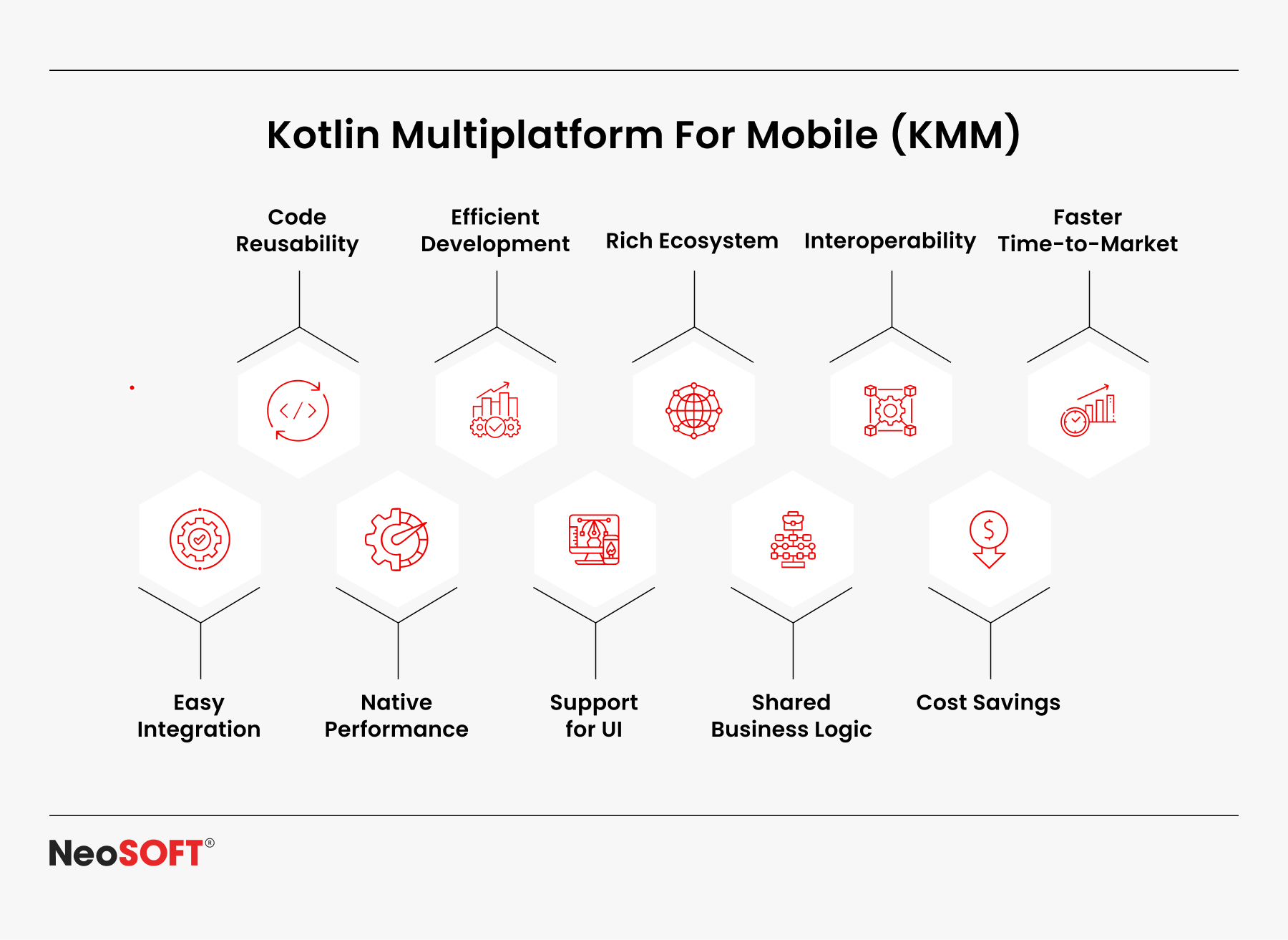
Kotlin Multiplatform For Mobile (KMM)
Developers can collaborate on sharing fundamental business logic between iOS and Android while creating native code for platform-specific features whenever required, with the help of KMM. The development of scalable and high-performing apps is made possible or encouraged by this blend of native and shared development.
Primary advantages include:
- High-performance native apps are made possible by direct access to native APIs on iOS and Android.
- Strong Kotlin language features that increase efficiency and decrease errors include type inference, coroutines, and null safety.
- Robust assistance from JetBrains and Google, with expanding community involvement and changing documentation.
- A flexible approach to managing Windows, Linux, and macOS platform-neutral projects. With 22% of Kotlin developers presently using Compose Multiplatform, JetBrains’ State of Developer Ecosystem 2023 report shows that Kotlin’s UI-sharing features are expanding across desktop, web, Android, and iOS.
- Enabling enterprises and professional Android developers. KMM is particularly well-suited for enterprise-grade apps, long-term scalability, and the ability to reuse shared business logic across platforms while preserving the benefits of native programming.
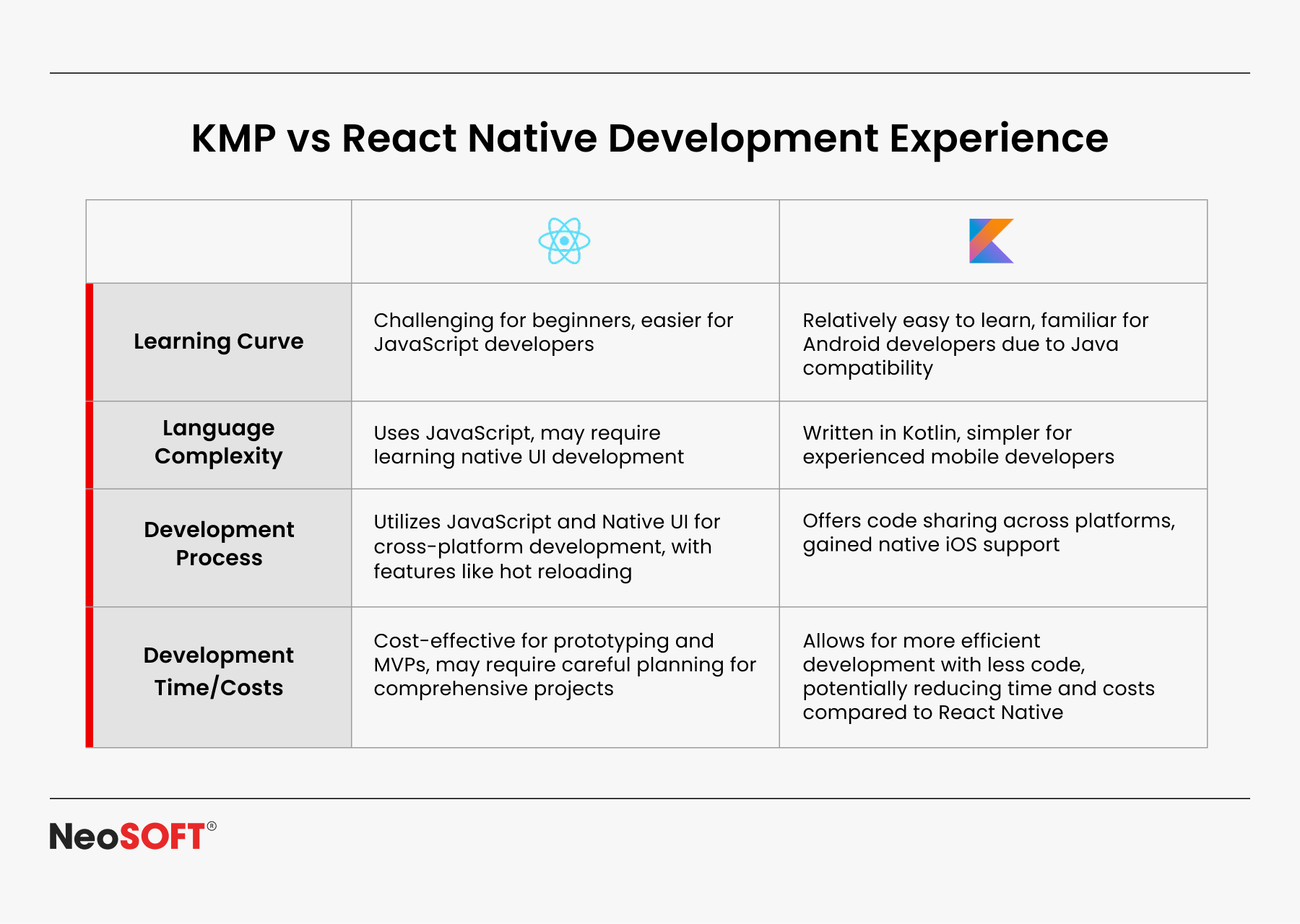
Learning Curve & Developer Expertise
A company’s grasp of language and technology largely determines the learning curve.
React Native: Utilizing the same code for iOS and Android, developers who are already familiar with JavaScript and React may create apps with ease.
Teams that have prior experience with the internet no longer have to start from zero when creating mobile apps. The simple user interface architecture, user-friendly elements, and active community speed up project implementation and lower initial barriers.
Kotlin Multiplatform: For Android developers, Kotlin is a natural fit; its integrated features, such null safety and coroutines, make code faster and more reliable.
Extending the scope beyond Android to iOS, desktop, Linux, or servers creates a new challenge. Native code, SDKs, and APIs must be successfully integrated. Although it may take longer to set up, the advantages – software that is more stable at the core, simpler to maintain, and far less prone to errors over time – make the effort worthwhile
Key Comparison Factors
1) Development Speed & Productivity
React Native: Making use of the same code for iOS and Android substantially shortens deployment times for teams that are familiar with React and JavaScript. Quick refresh, pre-built components, and an established declarative UI basis all help to enhance workflow and speed up debug cycles.
Kotlin Multiplatform: The initial setup is slower since Kotlin code must be connected to native code, SDKs, and platform APIs. However, sharing core logic across different platforms reduces duplication. Advanced Kotlin language features (coroutines, null safety) provide reliability and fewer bugs in native programming.
2) Performance
React Native: Provides performance that is almost native for the majority of mobile applications. Tasks involving a lot of graphics or computation could need special native code modules for optimization.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Compiles to true native apps via JVM/LLVM. Direct access to platform APIs ensures smoother animations, faster load times, and optimized screen responsiveness across operating systems.
3) UI/UX Capabilities
React Native: Owing to a large ecosystem of reusable parts and UI libraries, it is flexible for cross-platform design. Also, certain platform-specific peculiarities can necessitate the use of extra native code.
Kotlin Multiplatform: SwiftUI/UIKit and Jetpack Compose, respectively, offer apps on iOS and Android entire native control over the user interface. This gives developers the ability to design platform-neutral experiences.
4) Integration with Existing Systems & Tooling
React Native: It makes use of popular editors like VS Code and IntelliJ, the JS toolchain (Node, NPM/Yarn), and OTA update options. It connects to REST/GraphQL backend APIs with ease. Native bridges connect to SDKs when deeper integration is needed.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Interacts with Android Studio and Gradle for Android development and CocoaPods/Xcode for iOS app development with ease. Since Java and modern programming tools are very compatible, projects can expand across desktop (Windows, Linux, macOS), server, and other operating platforms.
5) Community & Ecosystem
React Native: Backed by a large, global community, with extensive documentation, frequent contributions, and many open-source library versions used by leading companies.
Kotlin Multiplatform: A younger but rapidly growing multiplatform ecosystem. Strong backing from Google and JetBrains, along with active developers improving documentation and tools.
6) Future Scalability & Maintenance
React Native: Permits quick cross-platform delivery; nevertheless, a significant dependence on other repositories and libraries may result in long-term maintenance issues for various versions.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Centralized shared Kotlin code minimizes recurrence. Its close alignment with native stacks simplifies updates and long-term support across different operating systems.
7) Security & Compliance Considerations
React Native: Framework dependencies need to be audited as they depend on numerous libraries and external components. Additional native code might be required for regulated APIs, encryption, and safe storage of sensitive data.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Grants direct access to security features at the platform level. Also, it works well for creating enterprise-grade, compliant apps where security is a top priority when paired with native toolchains and Kotlin language features.
8) Cost Implications
React Native: Economical for quick multi-platform rollouts and MVPs. Teams with JavaScript/React developers can quickly contribute without major retraining.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Entails a substantial investment cost, but it lowers ongoing costs by reducing errors, streamlining processes, and permitting code reuse across desktop, web, and mobile applications.
Use Case Scenarios
The project type, target platforms, and overarching business objectives all influence the most effective framework. Each alternative offers advantages that correspond to certain developmental requirements.
React Native is best for:
- Start-ups and SMEs: Create MVPs and prototypes for web, iOS, and Android apps rapidly using the same code. The time to market ratio is lowered, and start-up costs are lower.
- Companies focused on speed: Appropriate for tasks that need rapid development cycles, regular updates, and accurate debugging processes.
- Teams with web expertise: Teams already familiar with JavaScript, React, and reusable components can transition smoothly into mobile app creation across multiple platforms.
Kotlin Multiplatform is best for:
- Enterprises and large-scale apps: Curated for building native applications when security, reliability, and compliance with industry standards are crucial factors.
- Feature-rich applications: The most effective apps are those that actively rely on native iOS frameworks and Jetpack Compose for Android, feature complex workflows, or have sophisticated user interfaces.
- Long-term, multi-platform strategies: Easy to maintain and simple. Additionally, it supports an array of operating systems, such as servers, Linux, Windows, macOS on PCs, iOS, and Android.
Prospects for the Future and Industry Adoption
React Native: React Native is steadily improving performance through increased native code integration, new APIs, and enhanced developer tools, with the help of Meta and a large open-source community. Owing to their ability to create the same code for iOS, Android, and web apps, it has become a superior choice for companies that wish to use a single repository to access many platforms.
Kotlin Multiplatform: Thanks to assistance from Google and JetBrains, it is becoming more and more well-liked in professional and enterprise Android development. The Jetpack Compose framework is an excellent choice for those developing complex, long-term solutions for various operating systems, given its multi-platform features, increased Java interaction, and support for desktop (Windows, Linux, macOS) and server-based applications.
While React Native will continue to be the preferred option for cross-platform apps and short projects, Kotlin Multiplatform is expected to establish itself as the standard for economically viable and critical solutions that need native programming and strong collaboration with the current technology stack in the future.
Problem-Solving Framework
The manner in which the framework satisfies technical specifications and business goals will determine whether Kotlin Multiplatform or React Native is selected. Important elements consist of:
Timelines & speed: React Native accelerates app development with the same code for Android, iOS, and even web applications. Kotlin requires more setup but delivers stable native apps for long-term projects.
Budget & resources: Teams with JavaScript and React developers can cut costs using React Native. Kotlin may need a higher upfront investment, but it reduces bugs and improves maintainability across different platforms.
Performance & UX: The majority of consumer apps work well with React Native, although it could lag on important screens or jobs requiring a lot of graphics. Kotlin guarantees improved efficiency and a nicer user interface with native code and Jetpack Compose.
Scalability & maintenance: React Native depends on regularly updated versions and third-party libraries. Supported by Google and JetBrains, Kotlin provides longer-term support and better Java interoperability.
Assessing these aspects aids businesses in developing apps that are optimized, guaranteeing cross-platform compatibility, and selecting the framework that best suits their approach.
Conclusion
In the highly competitive mobile app development scenario, choosing a framework is a crucial company choice. Since React Native facilitates multi-platform compatibility, rapid development, and the support of a strong JavaScript/React developer community, it can be utilized by small services and businesses having shorter launch times.
The KMM framework is a top pick for companies wishing to develop safe, effective, and sustainable apps for the desktop, iOS, and Android platforms because of its comprehensive Kotlin functionalities and native equivalent speed.
Your ability to develop optimized apps, satisfy customer expectations, and offer regular assistance across several platforms could all be impacted by your decision between these two approaches.
Using the framework that best suits your business’s requirements, our team of skilled mobile developers and experts can assist you in developing scalable solutions. Contact us at [email protected] to explore how we can help with your forthcoming project. Partner with us today, to build secure, high-performing apps tailored for iOS, Android, and other platforms.