Swipe to the Future: E-Wallets and the Rise of Smart Fintech Solutions
Introduction: The E-Wallet Shift In Payments
Smartphones and tablets, digital-first consumers, and the rising need for contactless, real-time payments are all propelling the banking industry’s swift transformation. Digital payment options are changing how consumers handle banking operations across many platforms as physical use of currency diminishes.
This blog is an extensive resource for product managers, innovators, and CTO’s at payment facilitators, financial institutions, and fintech companies. Whether you’re developing a wallet app, introducing a virtual banking platform, or streamlining an existing payment system, you’ll learn how to keep up with regulations, safeguard private information, and provide an intuitive user experience that appeals to your target audience.
The key components of successful digital payment systems, standard software development processes, and practical advice for raising customer satisfaction, increasing payment acceptance, and adhering to international compliance standards will all be covered in the upcoming blog.
Understanding E-Wallets and Their Business Value
To facilitate quick and easy online transactions, an electronic wallet is a safe mobile or web-based application that retains payment details such as credit card numbers and savings account information. Users can transfer capital, make contactless payments, and manage their accounts via mobile or banking apps owing to these platforms’ support for a variety of digital payment methods.
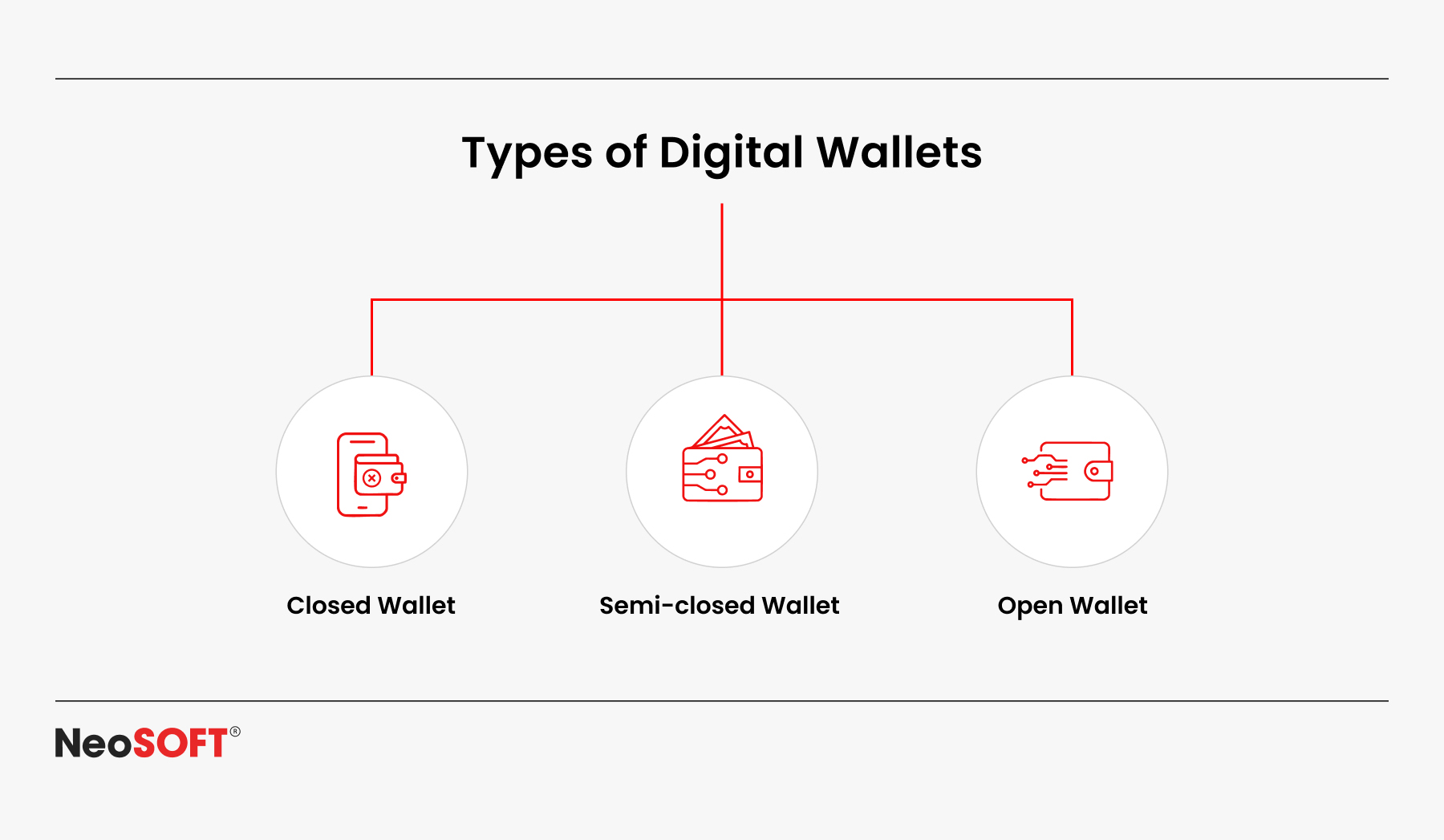
The majority of e-wallets fall into one of three categories: closed (single merchant), semi-closed (selected partners), or open (associated to bank accounts and employed on several platforms). Contactless payments such as mobile wallets are crucial for providing safe and practical payment experiences because of their versatility.
Employing biometric and multi-factor authorization, as well as real-time account management, a robust wallet software provides businesses with faster banking operations, reduced transaction fees, and a better experience for consumers. Furthermore, they facilitate revenue development through premium features, loyalty programs, and insights obtained from transaction history and consumer data.
Banking organizations, transaction handlers, and any organization catering to today’s digital-first customers must invest in safe, flexible, and user-friendly digital payment solutions due to the rise in mobile payments.
Core Components of a Digital Payment System
Banking organizations, payment gateways, and any businesses catering to today’s digital-first customers must invest in safe, flexible, and straightforward online payment solutions due to a surge in mobile transactions.
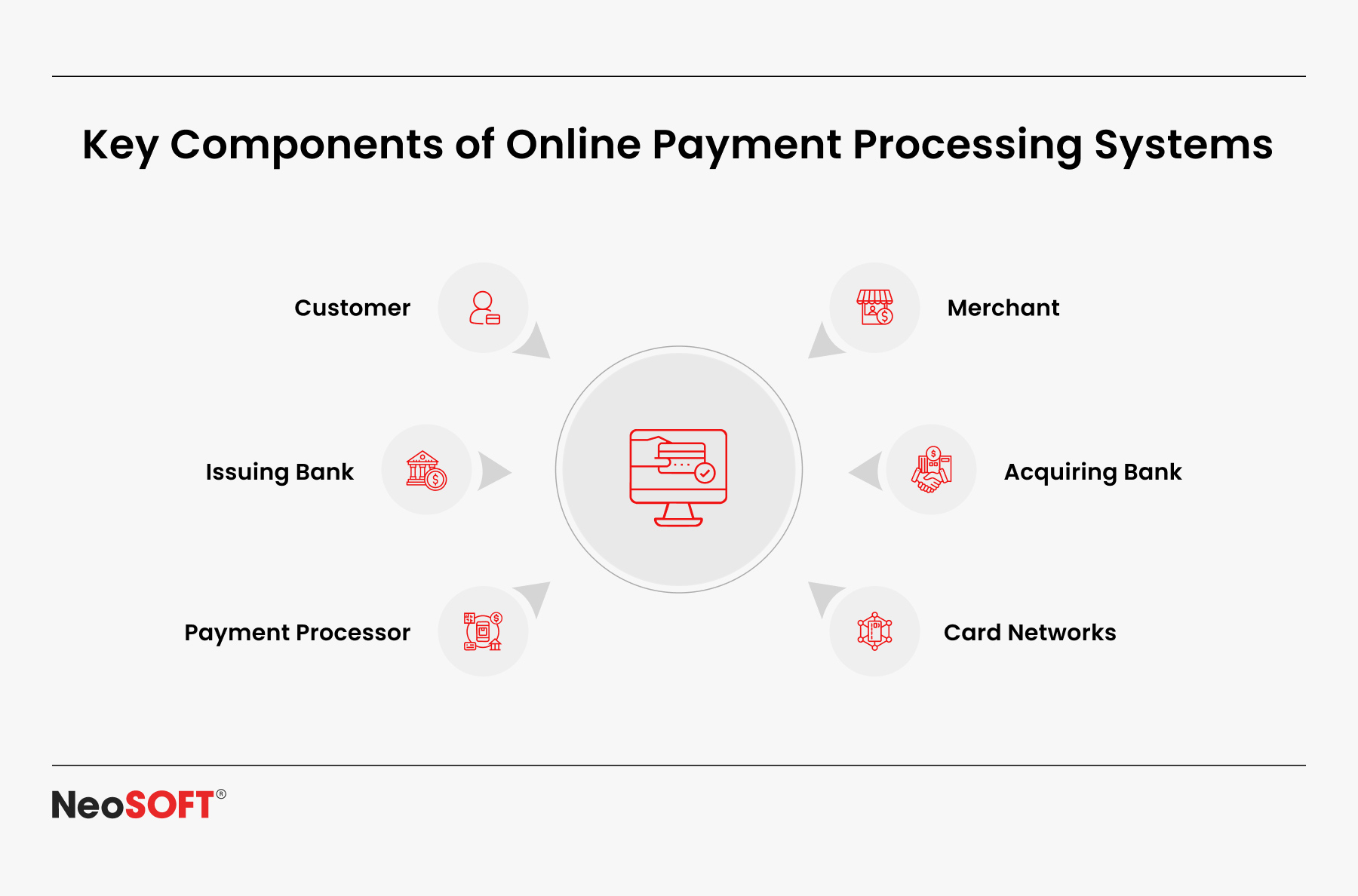
Integration of payment processing systems, which encrypts and transmits payment data, especially credit card and bank account information, is vital for this. This provides safe payment acceptance, safeguards confidential data, and permits effortless interaction with third-party providers.
Accessibility on all handheld gadgets is maximized by ensuring seamless integration throughout web and mobile platforms. This results in a durable, scalable, and intuitive platform when complemented by biometric authentication, two-factor authentication, and other advanced security features.
These elements serve as the fundamental components of a safe, modern electronic payment platform made to satisfy changing customer demands and business demands.
Third-Party Integrations: Expanding Wallet Functionality
In modern times, successful digital wallets do significantly more than just store data from credit cards or allow contactless payments. They act as centers of finance, allowing easy access to outside resources and services that enhance every aspect of the payment procedure.
Integration with third-party payment gateways such as Google Pay and Apple Pay simplifies online transactions and ensures broad payment acceptance. Meanwhile, linking with loyalty programs, billers, and financial planning tools enables end users to do more than just transfer money; they can manage their entire financial life cycle from a single mobile app.
For payment processors and developers, enabling third-party integrations unlocks advanced features such as biometric authentication, customized account management, and even cryptocurrency wallets. When done correctly, these user interfaces provide an effortless transition into an intuitive environment that supports an assortment of bank card types and payment methods.
Fintech companies have the ability to provide a consistent, safe, and compliant solution across customer groups, mobile devices, and geographical locations by allowing customers to access various financial services through a single wallet app.
Security First: Ensuring Safe Transactions
Techniques for end-to-end encryption and coding are crucial for protecting payment data, especially when utilizing third-party services. One-time passwords and biometrics are two components of multi-factor confirmation, which minimizes criminal conduct and prevents unauthorized access.
Understanding international legal mandates as well as security guidelines guarantees adherence and fosters user confidence. Transactional monitoring, risk assessments, and real-time fraud detection all aid in spotting irregularities and responding against changing threats.
Everyday operations and system architecture need to incorporate security. In addition to safeguarding client data, a secure platform promotes scalability, compliance, and confidence across all payment systems.
Integrating AI and Machine Learning for Smarter Payments
Electronic payment services are being revolutionized by computational intelligence, artificial intelligence and machine learning, which make it possible to analyze transaction history, client preferences, and behavioral trends intelligently. This helps financial organizations and payment processors to offer more personalized, scalable, and secure services.
Anomaly detection driven by ML powers real-time fraud and automated risk assessments, reducing exposure to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive data like credit card and bank account information.
Additionally, AI powers recommendation engines that provide cognitive alerts, budgeting recommendations, and flexible user interfaces, which improve the mobile banking and wallet apps. Across a range of consumer categories, these insightful observations increase user satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
Platforms remain competitive by incorporating AI and ML into the development process, assuring that mobile payment systems and digital wallets are intelligent, safe, and optimized for use on an array of mobile platforms and devices.
Scalable Architecture for High-Performance Apps
The key to attaining scalable growth without interruption is implementing a modular, cloud-native structure. This strategy has a number of important benefits:
- Elastic Infrastructure: Permits on-demand resource scaling, guaranteeing your application can effectively manage high workloads and traffic spikes without experiencing performance deterioration.
- Offline Sync Capabilities: Facilitates data synchronization after the connection is restored, supporting a continuous user experience in areas with spotty or poor internet connections.
- Microservices Architecture: Diminishes downtime and speeds up feature rollouts by supporting the autonomous creation, deployment, and updates of individual modules.
In addition to maintaining excellent performance under escalating loads, such scalability makes it possible to incorporate new payment methods, loyalty plans, and cutting-edge financial technologies without endangering the system’s security or user experience.
Customizing for Global Markets and Regional Compliance
Infrastructure, regulation, and strategic specialization are necessary for the worldwide growth of digital payment systems. When tackling diverse markets, it’s critical to make changes to language preferences, set transaction limits, and personalize the customer’s interface for different kinds of customers.
Avoiding fines and fostering consumer confidence, regulatory compliance with regional legal standards including AML, KYC, and data protection is crucial. Risks during expansion are decreased by including these regulatory standards throughout creation and real-time reporting procedures.
Technically speaking, a cloud-supported modular architecture offers quick scaling, relatively low latency, and consistent uptime across geographical boundaries. Integrating with local payment methods and banks ensures smooth induction and payment acceptance.
Businesses could develop high-performance, scalable, and compliant electronic payment services for a variety of different international markets by investing in user study and legal counsel relevant to a given location.
Core Applications of Blockchain in Digital Payments
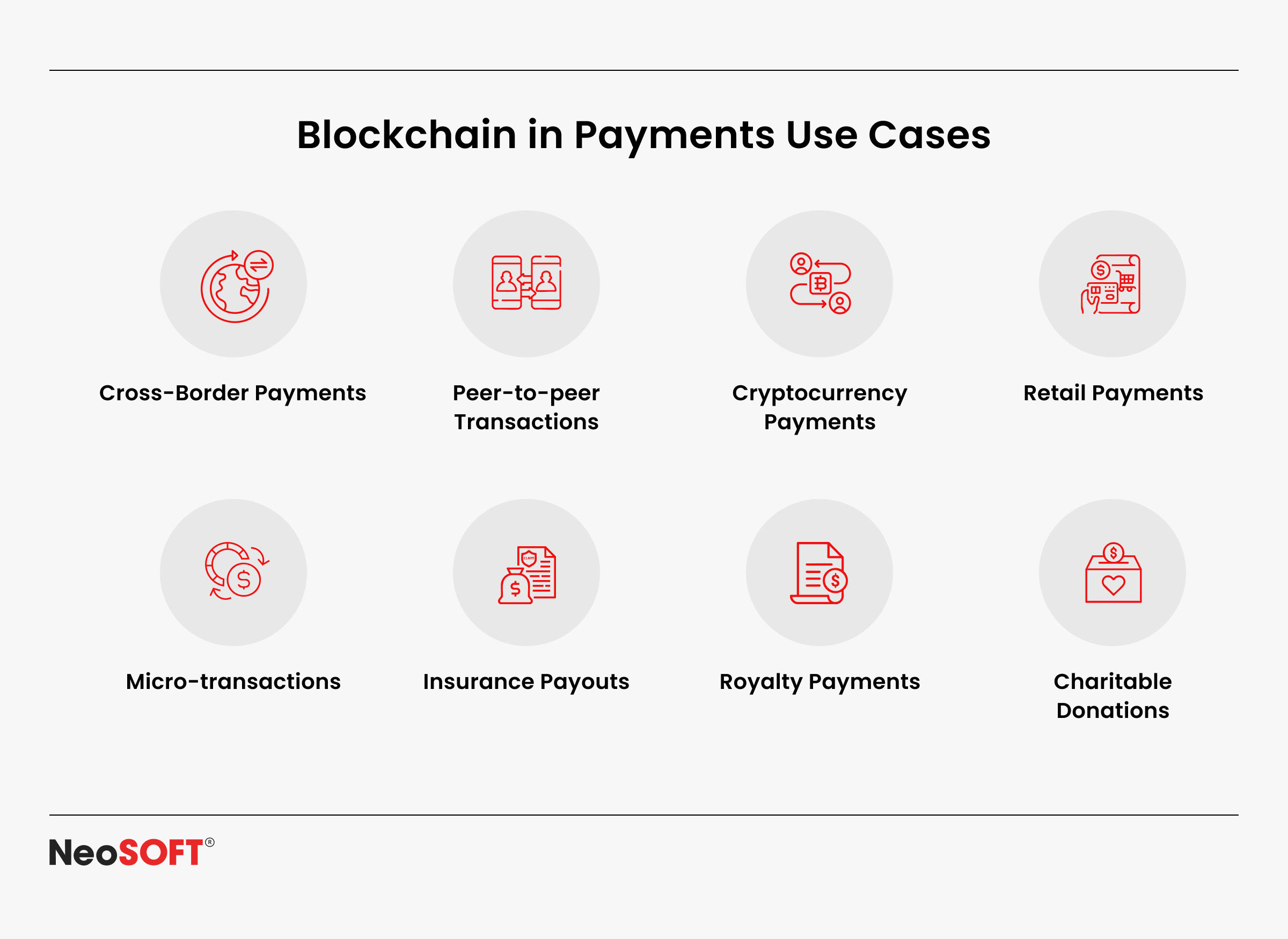
1. Crypto Wallet Development
Existing digital currency wallets combine user-friendly features like multi-device sync, personalized graphs, and immediate form portfolio management with safe features like cold storage and biometric authentication. These safeguard digital assets while improving the general consumer experience for audiences across the country.
2. Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Platforms
DeFi platforms leverage smart contracts to save costs and improve asset control, allowing consumers to lend, take out, and earn income without the use of traditional banks. They increase access to international financial resources, particularly in areas that are underserved by traditional banking, and they operate around the clock.
3. Cross-Border Payments and Digital Currency
By removing middlemen and significantly reducing down on transaction costs and delays, blockchain-based systems simplify international payments. The rise of digital currencies promotes financial inclusion by enabling faster transactions and more access to international markets.
4. Identity and Access Management
Blockchain improves privacy while adhering to KYC and AML standards by enabling safe credential transfers without disclosing all user information. Users can manage their digital identities across several sites with decentralized identity systems, which can minimize data leaks.
5. Security and Resilience
Even during network disruptions, blockchain’s decentralized architecture ensures unbroken uptime and tamper-proof transaction records. When combined with encryption and real-time validation, this enables secure, large payments across digital payment networks.
Overcoming Challenges in Adoption
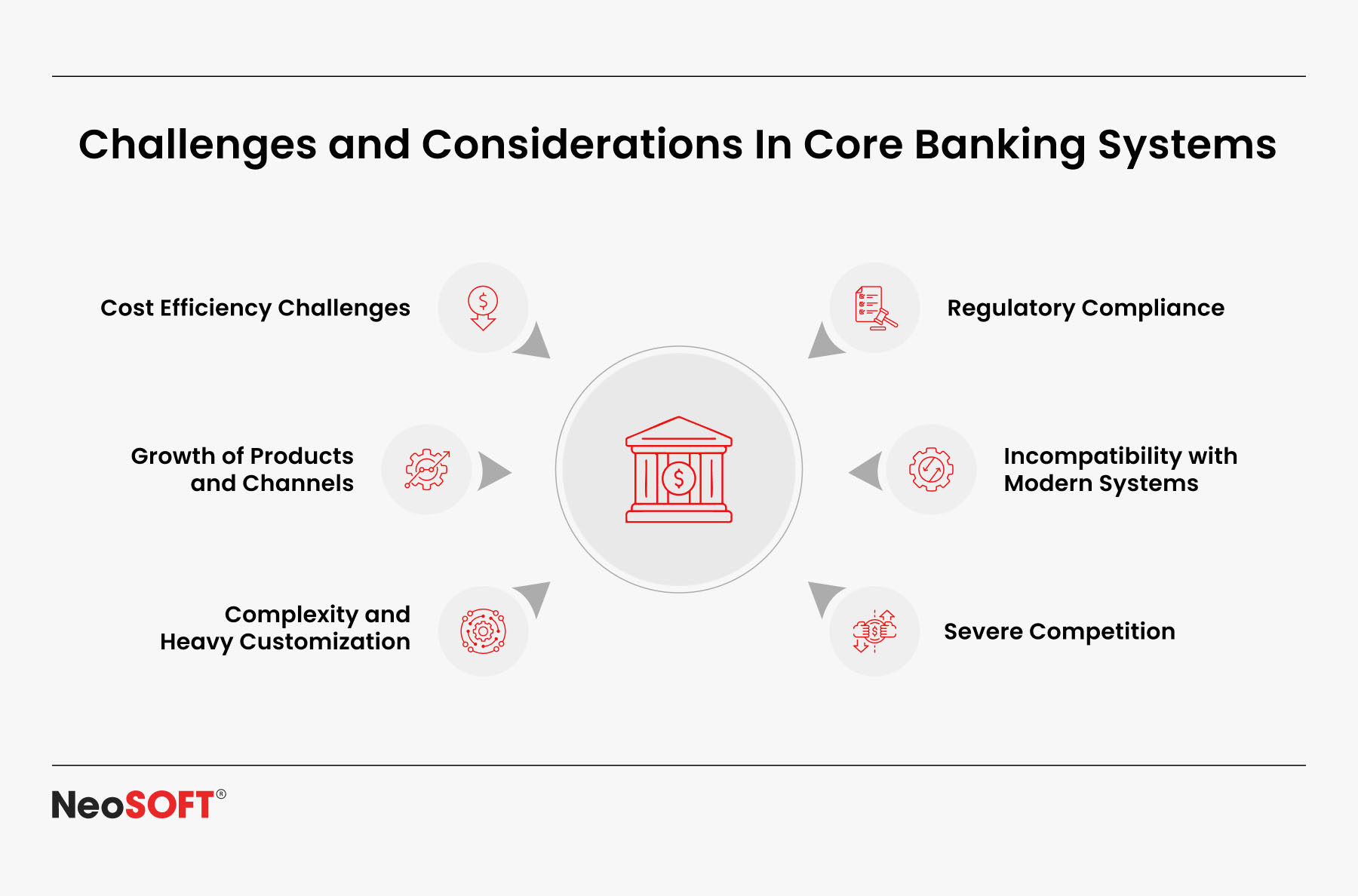
Although mobile payments and digital wallets are expanding quickly, financial institutions, tech startups, and payment processors may face certain difficulties when incorporating and expanding digital payment systems.
User Education
Important security features like biometric authentication, two-factor authentication, and their significance of preventing habits like using the same password again are still unknown to many users. Safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining long-term confidence in digital payment methods require educating consumers on how to secure their mobile devices, update their account information, and spot phishing efforts.
Balancing Security with Usability
It’s difficult to give users an intuitive user interface without compromising strong security protections. While insufficient safety can put bank account details, credit card information, and payment information at danger, excess friction points can harm the consumer experience. Smart authentication methods, which includes fusing device-based verification with biometric authentication, can provide safe and easy access to wallet, banking, and mobile apps.
Regulatory Complexity
Conformity to regulations is a dynamic goal, particularly for platforms that operate internationally and cater to various client segments. Meeting the evolving legal requirements for information protection, AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and KYC (Know Your Customer) for online financial transactions requires a deep comprehension of the regulatory landscape.
Device and Platform Scalability
It is essential to optimize performance across a variety of cellular devices, screen sizes, and operating systems. The platform must function consistently whether users are using an exclusive banking app, Apple Pay, or Google Pay to make payments online. Interoperability across a variety of platforms necessitates scalable backend infrastructure, often hosted on services like Google Cloud, and thorough testing for anything from iOS mobile banking apps to Android mobile wallets.
Optimizing Transaction Fees and Monetization Strategies
It’s critical for understanding how to strike a balance between affordability and profitability as mobile banking apps and digital wallets gain popularity. Optimizing transaction costs has a direct impact on user adoption and the long-term viability of businesses, whether it is done through a fixed price structure or variable prices depending on transaction limitations and customer behavior.
Many payment systems are moving toward tiered monetization strategies, where core digital payment methods remain free or low-cost while advanced features or cross-border money transfers incur nominal fees. This structure allows financial institutions and fintech platforms to serve customers across income brackets while still generating revenue.
Reducing transaction fees for frequent online payments or bundling services into cost-effective packages can further drive adoption. Businesses can also monetize valuable insights derived from transaction history and customer data to create targeted campaigns or premium account offerings.
Conclusion: Powering the Next Generation of Digital Payments
Digital payments contribute to the fast evolution of the fintech ecosystem. Enterprise-grade security, user-centric design, and scalable architecture enable companies to develop platforms that are both creative and compliant.
Payment apps and digital wallets have grown into a competitive advantage as opposed to merely a convenience. Financial institutions that make advances in cross-platform, future-ready solutions that provide security and performance will be the ones that thrive.
Businesses must prioritize long-term value creation over functionality if they’re going to succeed in these changing times. This includes developing platforms that satisfy legal standards, provide smooth user experiences, and permit cutting-edge features like fraud detection, AI-driven insights, and multi-device compatibility.
Our next-generation fintech innovation abilities will enable you to take advantage of the upcoming era of increasingly advanced, secure, and expandable digital payment systems. Get in touch with us at [email protected] now to find out how our payment systems and smart wallet solutions can enhance your digital services and increase client trust.