The Strategic Shift: Building Scalable Apps with Kotlin Multiplatform
Introduction
As cross-platform development accelerates, companies are required to overcome the barriers caused by single-platform development. For apps on iOS, Android, and various other similar frameworks, platform optimization is also essential. However, using traditional methods require creating the same application twice, resulting in redundant effort, longer development times, and increased maintenance costs.
This blog will help business leaders and Android developers to consider migrating to KMP as part of their long-term success plan. Moreover, it will describe its functions and how it can accelerate the development of native performance applications. If you are working on an Android app and wish to port it to iOS with less labor, or want to scale your KMP projects into other platforms, this will prove to be beneficial.
KMP doesn’t substitute for the native ecosystem, unlike frameworks like React Native. In fact, it permits you to write platform-specific solutions if required while exchanging common code and business logic across platforms. With this new model, you may use a constructed multiplatform approach for UI coherence, employ native code for unique device features, and create apps that function flawlessly on iOS and Android.
We will go over the basics of Kotlin Multiplatform, how it’s used in actual projects, its advantages and disadvantages, and the reasons why more businesses are using KMP for cross-platform projects in the parts that follow.
What Is Kotlin Multiplatform?
JetBrains’ open-source KMP framework, supported by Google, enables developers to construct identical code once and use it across desktop, iOS, and mobile apps for Android, among other platforms. Teams can exchange business logic using a shared module rather than keeping separate Android and iOS projects; however, they continue to produce platform-specific code when necessary.
This makes it easier for Android developers to produce iOS apps. Through Kotlin multiplatform migration, common components like the data layer or networking logic can be moved into a shared codebase, while UI and device features remain platform-specific implementations.
Key highlights of Kotlin Multiplatform projects:
- Shared codebase: Reuse Kotlin code for networking, authentication, and the same business logic across multiple platforms.
- Platform flexibility: Access platform-specific APIs with native programming and integrate native code when required.
- Seamless integration: Build Kotlin multiplatform projects in Android Studio, export native binaries for the iOS app, and integrate with existing workflows.
- UI support: Use Jetpack Components or Compound Multiplatform to ensure a uniform design across several platforms.
KMP provides native performance, eliminates duplication, and helps companies construct programs that operate flawlessly on desktop, iOS, Android, and numerous other platforms.
How Kotlin Multiplatform Works in Real Projects
Two primary layers constitute a typical KMP project:
- Shared module: Includes common code such as data layer, networking logic, and reusable business logic. Here, developers can avoid redundant work by transferring business logic across various platforms.
- Platform-specific modules: Handle UI and platform-specific implementations for each target, such as Jetpack Compose for Android apps or Swift for an iOS app. These modules allow teams to access platform-specific APIs while preserving native performance.
In real-world cross-platform projects, this structure enables teams to:
- Reuse the same business logic for features like authentication, data storage, or API calls across Android and iOS apps.
- Build consistent interfaces with a composed multiplatform, while still customizing the design and functionality for different platforms.
- Leverage dependency injection, utilize open source libraries, and apply native code to connect to device-specific features.
This adaptable approach lowers operational costs and speeds production, thereby rendering it simple for Android developers to transition to iOS applications. KMP projects allow teams to create applications that operate seamlessly on desktop, iOS, Android, and numerous other platforms with a well-organized common codebase and platform-specific code for unique needs.
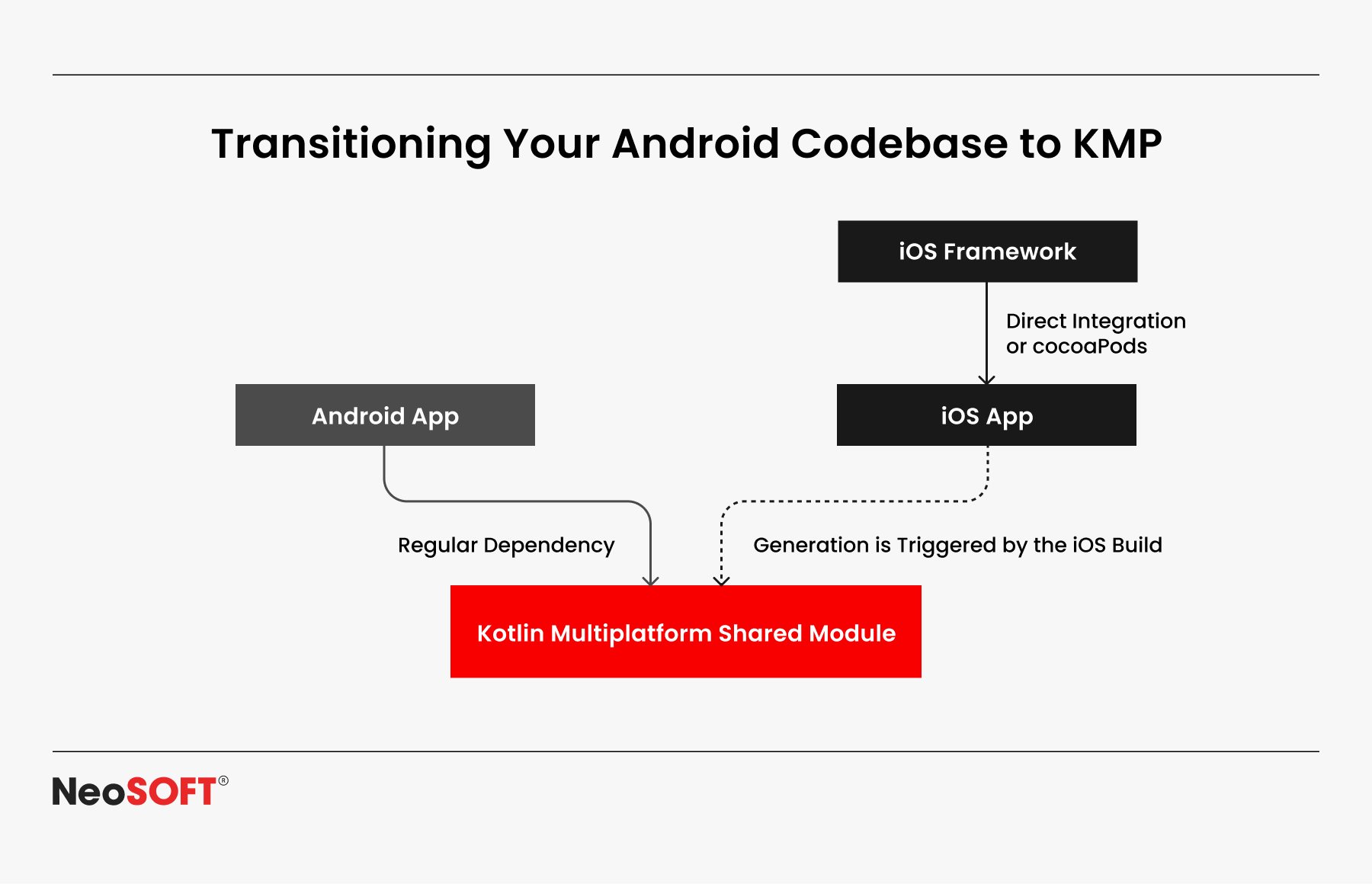
Transitioning Your Android Codebase to the KMP
Integrating Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) doesn’t require your current progress to be revamped. Beginning with the most crucial component, the migration can be implemented gradually.
Making a multiplatform module in Android Studio is mostly an early step in the process. The following phase is to combine elements like networking, authentication, and the data layer into a single codebase, which guarantees consistency across projects and makes upgrades easier in the future.
Linking the shared base with iOS development using Swift or Objective-C constitutes the next step. In order to utilize the shared functionality without interfering with current workflows, native binaries can be created. Teams can increase their adoption at a reasonable pace by gradually adding new features to the common module.
This progressive approach promotes them to be creative around cross-platform development without affecting dependability. Since information transfer decreases long-term maintenance costs, cuts down on duplication, and shortens release cycles, it is both strategic and practical.
This method improves code consistency, flexibility, and coherence within Android and iOS development teams, simultaneously streamlining the technical translation and encouraging teamwork.
Key Advantages of Kotlin Multiplatform
Code Reuse and Efficiency
One of the biggest benefits of KMP is the ability to write the same business logic once and then employ it in both iOS and Android apps. Developers can combine essential elements such as networking, authorization, and the data layer into just one module rather than running several Android and iOS projects.
This approach reduces redundancy while boosting code reuse and consistency in multi-module applications. This reduces the amount of repetitive coding and error-proneness for an Android developer who wishes to produce iOS applications. By leveraging a single codebase, teams may ensure a smoother workflow across numerous platforms, expedite releases, and save on development.
Lower Maintenance Costs
With KMP projects, bug fixes and updates are applied once in the shared code and automatically reflected across both Android and iOS apps. This lowers expenses and streamlines long-term support by doing away with the requirement to keep repetitive patches in distinct Android and iOS components.
This directly translates into more predictable project deadlines and reduced maintenance costs for businesses overseeing large-scale cross-platform initiatives. Companies that use Kotlin Multiplatform frequently discover that engineering resources may be diverted from tedious maintenance to innovation.
Seamless Integration with Native
KMP makes it simple for developers to combine native and Kotlin code, unlike frameworks that rely on JavaScript bridges like React Native. This suggests that while directly contacting platform-specific APIs and creating platform-specific code as needed, developers can still benefit from a single base of shared business logic.
The outcome is native performance driven by native binaries and Android, as well as the capacity to produce programs that function flawlessly on several platforms. To design rich, responsive user interfaces without sacrificing flexibility, teams can also employ dependency injection, open source frameworks, and contemporary solutions like Jetpack Compose or Compose Multiplatform.
Broad Platform Support
Kotlin Multiplatform KMP extends beyond iOS and Android. It allows businesses to develop apps for several platforms inside a single ecosystem because it supports desktop, online, and other platforms. Therefore, KMP is an effective choice for businesses seeking extensive cross-platform development because of its adaptability.
Businesses can grow more effectively, adjust to changing requirements, and guarantee consistent performance across all contexts by organizing work into KMP modules. The framework continues to expand as more businesses embrace KMP and contribute tools and libraries, enabling businesses to produce feature-rich, reliable apps more quickly while preparing for the future of multiplatform development.
Kotlin Multiplatform vs React Native
Kotlin Multiplatform (KMP) and React Native are two popular choices when examining cross-platform frameworks, regardless of the fact that they employ varying approaches to problem-solving.
- React Native: The runtime bridge that it utilizes helps it to connect JavaScript to native API’s. However, depending on a bridge might result in performance overhead, particularly in applications that handle a lot of data, use many animations, or have device-level interactions.
- Kotlin Multiplatform: Instead of utilizing an intermediary layer, KMP builds down to native binaries. This lets developers maintain crucial business logic consistency across projects, improve interaction with current toolchains, and gain direct access to device APIs. When KMP is used, apps function effectively, are more reliable, and require less periodic upkeep.
While KMP is favorable owing to its native speed, device customization, and effective code reuse, React Native can be used for situations where rapid development is more essential than optimization.
Risk Factors and Implications
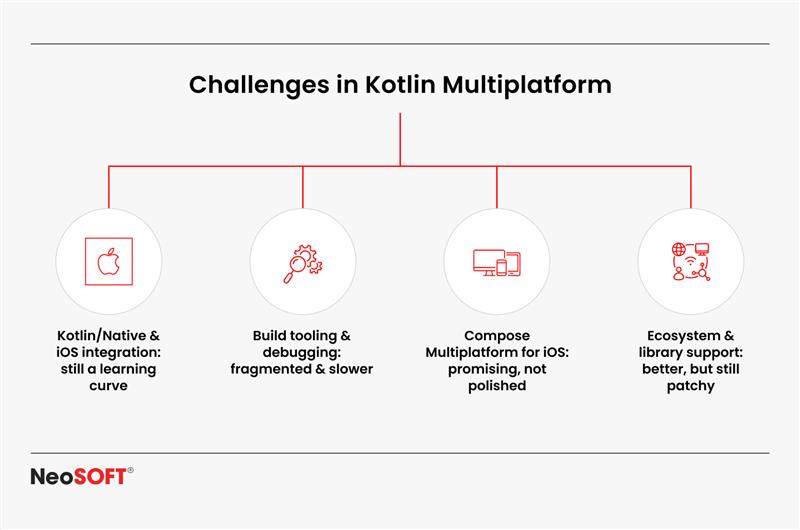
Learning curve: It may take some time for developers who are used to Android programming to acclimate to iOS apps and Objective-C compatibility. This is a frequent early adoption challenge, but with appropriate documentation and guidance, everything can potentially be made easier.
Tools and libraries: The ecosystem of open source libraries for KMP projects is growing, but it is not yet as mature as older frameworks. Teams often discover themselves combining community-driven technologies with customized solutions to deliver seamless adaptability as systems get more linked.
Platform-specific code: Push notifications, hardware sensors, and improved device storage are examples of features that require platform-specific implementations even with a resilient shared codebase. This implies that in order to ensure correct interaction with each operating system, developers must keep monitoring distinct Android and iOS apps for specific procedure components.
In spite of these factors, the adoption of KMP is growing fast. The developer coaching community is rapidly strengthening the ecosystem as more businesses invest in cross-platform projects and adopt open-source libraries.
The Future of Kotlin Multiplatform
Since one of the primary benefits of KMP is that it can be gradually used, it enables businesses to implement common modules without completely redesigning their systems. Through improving consistency in UI development across devices, frameworks such as Jetpack Compose and Compose Multiplatform are boosting adoption. Additionally, Android Studio’s enhanced tools and the constant expansion of open source libraries are facilitating teams’ experimentation, prototyping, and production scaling with less difficulty.
KMP initiatives are anticipated to offer definite commercial advantages as adoption increases, including quicker release cycles, reduced maintenance expenses, and increased team efficiency. As more businesses share success stories, trust in the framework’s long-term sustainability is growing.
Looking ahead, KMP’s future depends on striking a balance between flexibility and code reuse. KMP presents itself as a long-term answer for contemporary cross-platform development by allowing companies to reuse what is really important, such as networking, data processing, and security, while leaving room for customization.
Conclusion
More than just a framework, KMP is a calculated approach to contemporary app development. By allowing shared code reuse, reducing development time, and preserving native performance, it allows companies to create apps for desktop, iOS, Android, and other platforms without repeated labor.
Shorter release cycles, faster testing, and consistency are all advantages made possible for developers through integrating business logic into a single module. Additionally, by releasing teams from supporting disjointed codebases while focusing on developing new features, it enhances productivity and teamwork.
The advantages are obvious from a business standpoint: reduced maintenance costs, quicker time-to-market, and flexibility through progressive adoption. KMP can be implemented gradually by companies, integrating it where it is most beneficial and growing with confidence over time.
In the end, KMP facilitates more intelligent choices by striking a balance between scalability, performance, and cost effectiveness. To discover more on how it can assist you in developing scalable, high-performing applications specific to your sector, send us an email at [email protected]. The future of app development lies in adaptability. Connect with our experts today, to choose a smarter, more unified path to digital success with KMP.